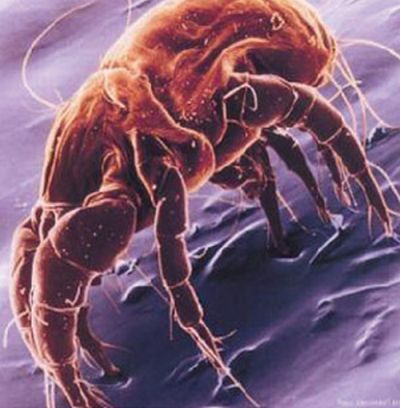
What are Dust Mites?
House Dust Mites are microscopic with an average size of less than 0.5 millimetres. They are a creamy white colour and belong to Arachnida (spider family). They thrive in warm, wet environments in the home, especially in bedrooms. Their characteristics include an oval-shaped body, no wings, light colouring with fine stripes and a life span of around two months or so, depending on conditions. The most common type of dust mite found in Australian homes is called Dermatophagoides Pteronyssinus and it prefers coastal, rather than inland regions. It is linked with skin and breathing allergies in humans, such as eczema and asthma. The House dust mites get their name from their habitat; household dust. The main element of dust is dead skin cells which is a mite’s preferred food source. Household items that get heavy usage like upholstered furniture, beds and carpets, have a higher mite population than other parts of the home.
More About Dust Mites
House Dust Mites get moisture from our perspiration and breathing and they feed on the dead skin cells that are shed in bedding. Humans shed about 1.5 grams of skin flakes and cells per day, or up to 0.45 kgs annually, which is sufficient to sustain vast populations of dust mites in every item of bedding. These dust mites can survive all climates, even at high altitude or in dry climates, surviving and reproducing with ease in your bedding due to the humidity generated by our human bodies.